The device consists of a pipe with transducers that emit and receive ultrasound signals into the flow of the medium.
The transducers used are either integrated transducers which consists of wetted transducers that come in contact with the fluid to be measured or Clamp-on transducers, which consists of transducers that are fixed externally to the pipeline.
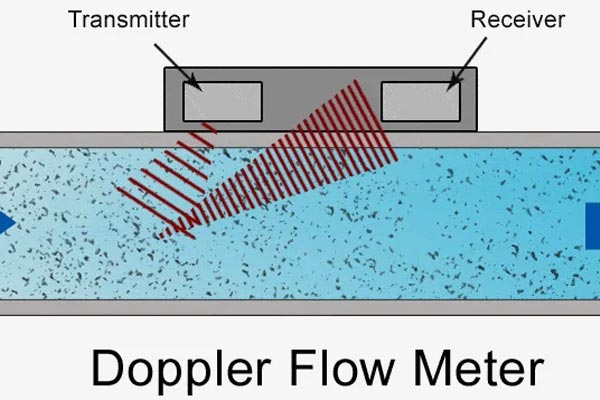
1️⃣ Doppler Flow Meter
This flow meter utilizes two piezoelectric transducers (either built-in or clamp-on) positioned at a fixed distance “L” apart. One transducer emits ultrasonic signals at a defined frequency. As these signals pass through the fluid, they are reflected by suspended particles or gas bubbles acting as acoustic reflectors.
The second transducer receives these reflected signals, which now exhibit a frequency shift due to the motion of the particles. This difference, called the Doppler frequency shift, is directly proportional to the flow velocity of the medium.
Since the pipe’s diameter is known, the system calculates the volumetric flow rate by combining the flow velocity and pipe cross-section data.
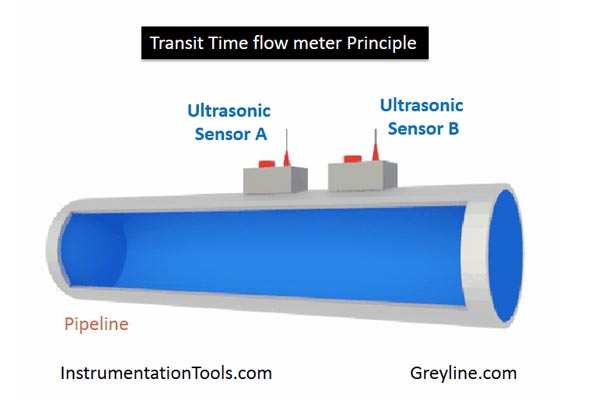
2️⃣ Transit Time Flow Meter
The transit time flow meter measures flow based on the difference in travel time of ultrasonic signals between two transducers placed a specific distance apart. Here’s how it works:
-
The signal travels downstream (with the flow) and then upstream (against the flow).
-
Because the downstream signal travels faster than the upstream signal, a time difference—known as the Transit Time or Time of Flight (TOF)—is detected.

